ACI2: Ultra-Early Warning and Adversary Identification with BDI Reasoning Agents
Introducing “Alcazar,” a meta-agent in our Reasoning Box for Bioneurocognitive Complex Reasoning applied to cyber defense and multi-domain operations
With this first “knowledge pill,” we begin to share -step by step- our lines of work in Bioneurocognitive Complex Reasoning Systems (BNC). This area of research is classified, in particular the design of our Complex Reasoning Architectures (CRAs) aimed at intelligence, strategy, and AI-driven operations across security, defense, and multi-domain warfare.
In this installment we introduce the modeling approach, purpose, and structure of a BDI Meta-Agent—ACI2 (Adversary Cyber-Intent Inference). We are building this meta-agent at Binomial Consulting & Design S.L., with the support of our military-AI lab WarMind Labs, operated with our partners at 1MillionBot in Torre Juana OST IA Hub, as part of our Reasoning Box program dedicated to cybersecurity and cyber defense, code-named “Alcazar.”
The meta-agent and its associated operational agents are designed to generate ultra-early alerts and conduct precise, automatic profiling of cyber attackers through hypothetico-deductive reasoning that incorporates both uncertainty and evidence. By the principle of “Reusability of Reasoning,” the same approach can be applied to other domains in security and defense and, more broadly, to scientific-technical reasoning contexts -medical, environmental, and beyond- where uncertainty and complex hypothetico-deductive reasoning carry high value. Critically, our architectures aim to deliver these capabilities pervasively and within milliseconds.
Certain implementation details remain classified.
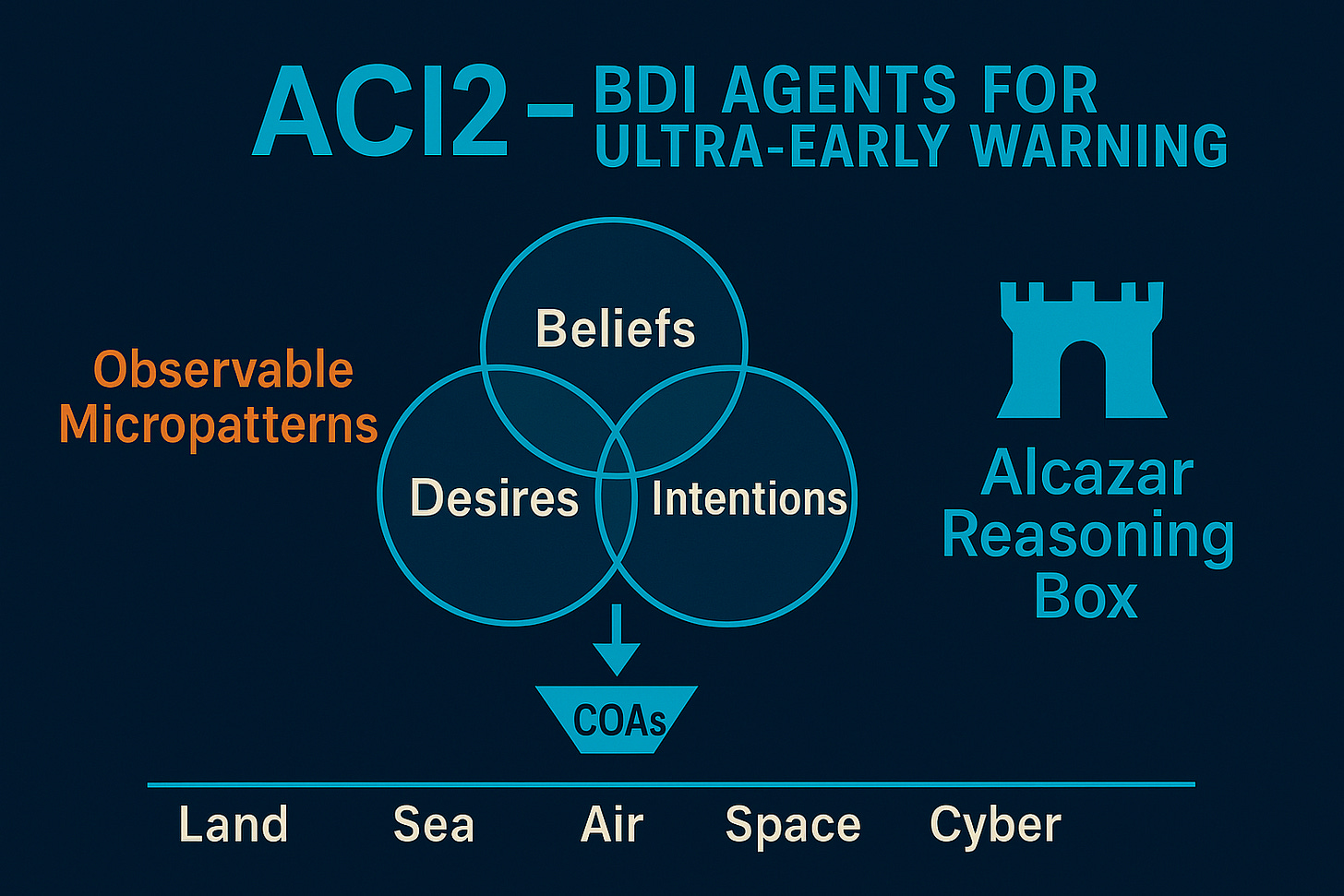
Figure: Alcazar Reasoning Box
BDI foundations: beliefs, desires, intentions
In Bratman’s BDI model, intentions are partial plans formed by an intelligent entity (here, a Meta Operational Agent) to pursue certain goals (desires), grounded in its perception of the world state (beliefs). That perception is bounded by the information -and associated uncertainty- available to the agent and by the reasoning processes encapsulated within it. In multi-agent systems, the ability to measure resident uncertainty is as important as the information about the world state the agent seeks to acquire; in some cases it is even more important. For classified research reasons, we do not elaborate further here. In BDI terms, intentions are a subset of desires on which the agent decides -or is tasked- to act.
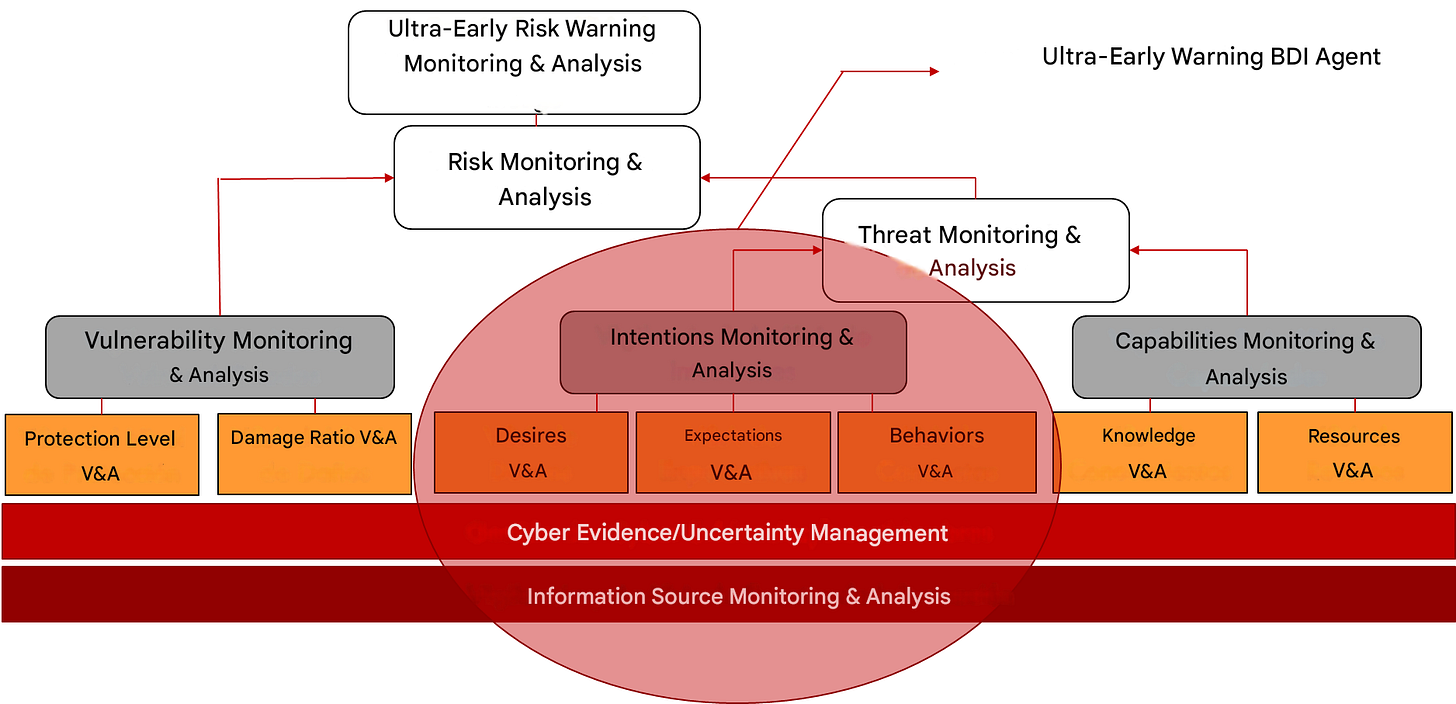
Figure: Meta-agent ACI2 within the Alcazar meta-agent structure.
Why BDI for cyber defense?
Within cybersecurity and cyber defense, BDI agents equipped with deductive reasoning models can deliver ultra-early warning about attacker behavior patterns and likely methods at very early stages, signals that are typically undetectable to today’s data-only approaches (and only partially captured by ontology-based systems).
Our dynamic knowledge structures for intention inference, realized through BDI agents, enable ultra-early detection for both single-phase and multi-phase, multi-domain cyberattacks—individual or concurrent. These structures surface what we call “Observable Micropatterns”: small, distributed indicators that, when cooperatively shared across a cyber protection network, compose the emerging attack pattern. This allows adaptive protection mechanisms and runtime reconfiguration of systems at risk.
When combined with available cyber threat intelligence about prior or similar attacks -structured and encapsulated as evidence-based reasoning agents (our internal SIL agents)- the ecosystem can help attribute attempts (successful or thwarted) to cyber-activist groups, cybercriminal organizations, or hostile nation-state cyber units.
The ACI2 model (Adversary Cyber-Intent Inference)
ACI2 is our extension and generalization of prior work by Geddes (Models for inferring human intentions of cybercriminal/cyberwarriors; paper forthcoming). It implements what we term “Reasoning Under Uncertainty in Multi-Agent Environments,” a necessity in modern real-time multi-domain warfare, where informational sufficiency, dominance, or superiority cannot be reached in the time available for planning, reflection, and action (the strategic, deliberative, causal, and decisional reasoning sequence in our complex reasoning systems).
In ACI2, uncertainty management blends, in a principled way:
Fuzzy logical reasoning (via neuro-fuzzy networks or structured fuzzy-set models),
Dempster–Shafer belief reasoning,
Possibilistic reasoning, and
Qualitative reasoning techniques.
Together, these enable a BDI meta-agent to formulate high-fidelity Courses of Action (COAs) for ultra-early warning of adversary behavior.
Reasoning from the adversary’s perspective
In ACI2, the “reasoning space” that the network of intelligent agents must cover for ultra-early warning and adversary identification is defined by both knowledge (informational certainty) and ignorance (informational uncertainty) about the cyber domain to be protected. This explicit treatment of ignorance is rarely considered pertinent in prevailing cybersecurity doctrine and only partially, if at all, in some recent cyber-defense doctrine. Unlike conventional systems that reason primarily from their own telemetry, ACI2 agents deliberately reason about what the adversary is likely to know and possess, looking through the adversary’s eyes instead of their own. This shift counters a common human bias that otherwise causes persistent errors and, at times, major failures.
Three streams of deductive hypotheses ACI2 must manage
Hypothetico-deductive reasoning that yields actionable knowledge about the motivations behind anomalous actions and behaviors expected to occur in a multi-domain context.
Hypothetico-predictive reasoning that anticipates next actions, the resulting changes in behavioral parameters inside and outside the protection network, and the objectives involved.
Hypothetico-deliberative reasoning that diagnoses procedural errors in operational playbooks and optimizes the reasoning processes of the participating BDI agents.
The “Alcazar” Reasoning Box
Within the Reasoning Box we call “Alcazar,” our goal is to create a network of reasoning entities that, in time-critical conditions and in an adaptive, evolutionary, and autonomous fashion, can assist the Cyber Commander in detecting indications of attack both outside and inside the perimeter of cyber protection and in adopting—automatically and/or under supervision, appropriate deterrence, protection, response, and forensic strategies.
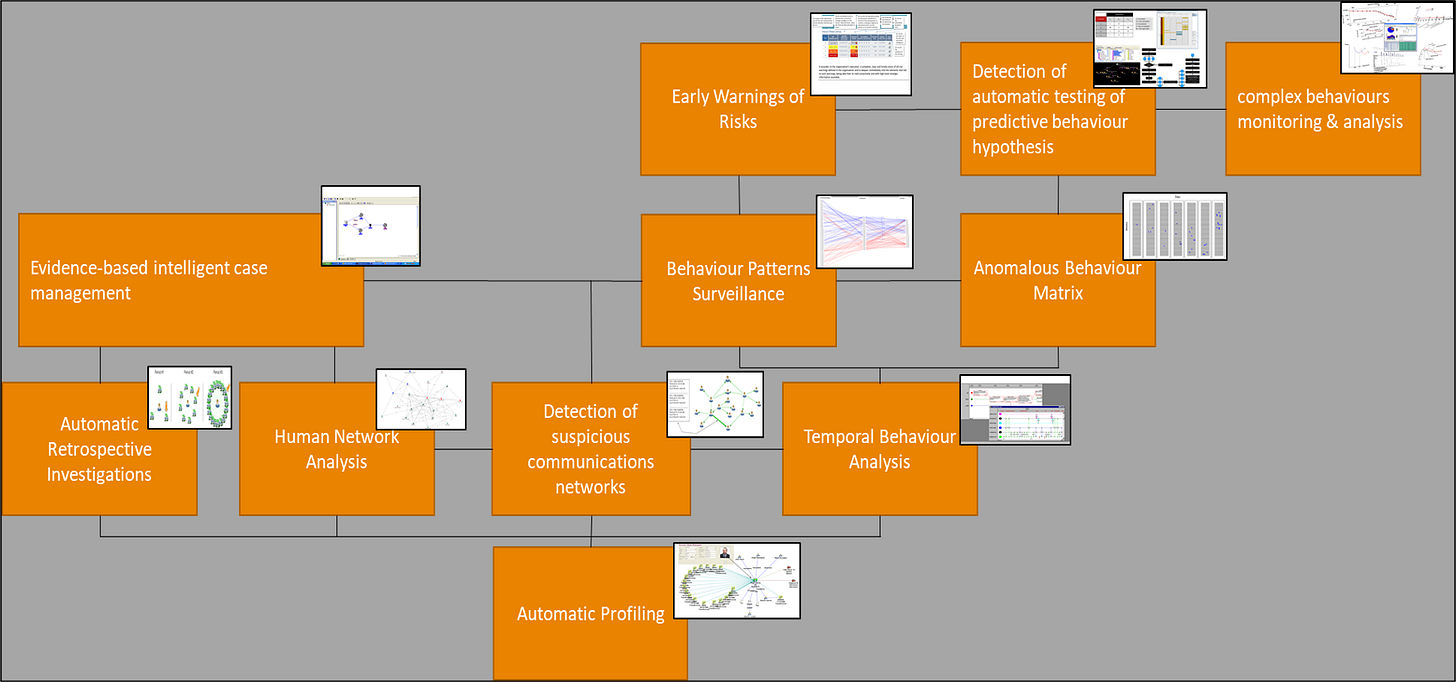
Figure: Holistic view of techniques supporting deductive reasoning in an ACI2 meta-agent inside the Alcazar Reasoning Box.
Closing note
As a classified project, we remain available to share more about our approaches, models, and progress in Bioneurocognitive Complex Reasoning Systems, applied to security, defense, and multi-domain warfare.
Author
Luis Martín “The Druid”
Senior Researcher, Designer, and Consultant of Advanced AI Systems. Founder, authority, and researcher in BNC Complex Reasoning Systems. Focused on designing CRAs for AEA Superiority Systems in security, defense, and warfare.
Principal Designer and Researcher at Binomial CD (www.binomialcd.com).
Vice President and Chief Visionary Officer at WarMind Labs (www.warmindlabs.com).